[1] Howitz, K. T., Bitterman, K. J., Cohen, H. Y., Lamming, D. W., Lavu, S., Wood, J. G., Zipkin, R. E., Chung, P., Kisielewski, A., Zhang, L. L., Scherer, B., & Sinclair, D. A. (2003). Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature, 425(6954), 191–196.
[2] Nadeeshani, H., Li, J., Ying, T., Zhang, B., & Lu, J. (2021). Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) as an anti-aging health product - Promises and safety concerns. Journal of advanced research, 37, 267–278.
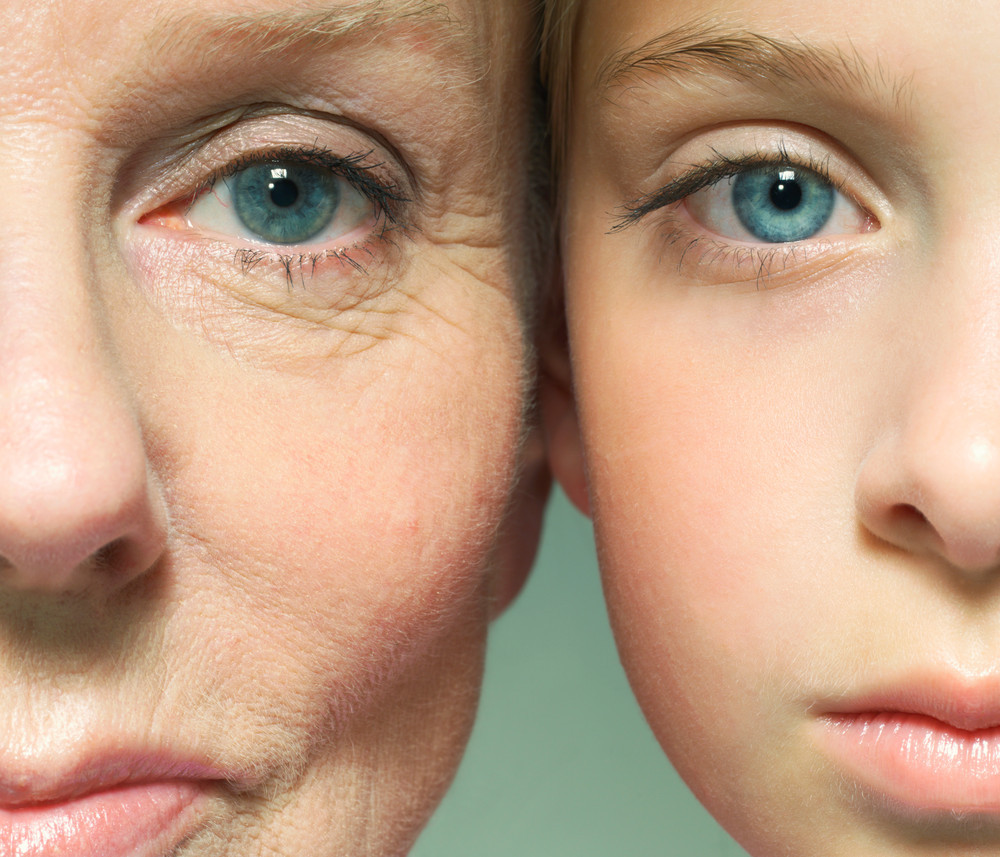
[3] Massudi, H., Grant, R., Braidy, N., Guest, J., Farnsworth, B., & Guillemin, G. J. (2012). Age-associated changes in oxidative stress and NAD+ metabolism in human tissue. PloS one, 7(7), e42357.
[4] Yoshino, J., Baur, J. A., & Imai, S. I. (2018). NAD+ Intermediates: The Biology and Therapeutic Potential of NMN and NR. Cell metabolism, 27(3), 513–528.
[5] Zhu, X. H., Lu, M., Lee, B. Y., Ugurbil, K., & Chen, W. (2015). In vivo NAD assay reveals the intracellular NAD contents and redox state in healthy human brain and their age dependences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(9), 2876–2881.
[6] Braidy, N., Berg, J., Clement, J., Khorshidi, F., Poljak, A., Jayasena, T., Grant, R., & Sachdev, P. (2019). Role of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide and Related Precursors as Therapeutic Targets for Age-Related Degenerative Diseases: Rationale, Biochemistry, Pharmacokinetics, and Outcomes. Antioxidants & redox signaling, 30(2), 251–294.
[7] Yoshino, J., Mills, K. F., Yoon, M. J., & Imai, S. (2011). Nicotinamide mononucleotide, a key NAD(+) intermediate, treats the pathophysiology of diet- and age-induced diabetes in mice. Cell metabolism, 14(4), 528–536.
[8] Cantó, C., Menzies, K. J., & Auwerx, J. (2015). NAD(+) Metabolism and the Control of Energy Homeostasis: A Balancing Act between Mitochondria and the Nucleus. Cell metabolism, 22(1), 31–53.
[9] Lu, Z., Jiang, L., Lesani, P., Zhang, W., Li, N., Luo, D., Li, Y., Ye, Y., Bian, J., Wang, G., Dunstan, C. R., Jiang, X., & Zreiqat, H. (2023). Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Alleviates Osteoblast Senescence Induction and Promotes Bone Healing in Osteoporotic Mice. The journals of gerontology. Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences, 78(2), 186–194.
[10] Chalkiadaki, A., & Guarente, L. (2015). The multifaceted functions of sirtuins in cancer. Nature reviews. Cancer, 15(10), 608–624.
[11] Wilk, A., Hayat, F., Cunningham, R., Li, J., Garavaglia, S., Zamani, L., Ferraris, D. M., Sykora, P., Andrews, J., Clark, J., Davis, A., Chaloin, L., Rizzi, M., Migaud, M., & Sobol, R. W. (2020). Extracellular NAD+ enhances PARP-dependent DNA repair capacity independently of CD73 activity. Scientific reports, 10(1), 651.
[12] qbal, T., & Nakagawa, T. (2024). The therapeutic perspective of NAD+ precursors in age-related diseases. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 702, 149590.
[13] Ratajczak, J., Joffraud, M., Trammell, S. A., Ras, R., Canela, N., Boutant, M., Kulkarni, S. S., Rodrigues, M., Redpath, P., Migaud, M. E., Auwerx, J., Yanes, O., Brenner, C., & Cantó, C. (2016). NRK1 controls nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinamide riboside metabolism in mammalian cells. Nature communications, 7, 13103.
[14] Yoshino, J., Baur, J. A., & Imai, S. I. (2018). NAD+ Intermediates: The Biology and Therapeutic Potential of NMN and NR. Cell metabolism, 27(3), 513–528.
[15] Niu, K. M., Bao, T., Gao, L., Ru, M., Li, Y., Jiang, L., Ye, C., Wang, S., & Wu, X. (2021). The Impacts of Short-Term NMN Supplementation on Serum Metabolism, Fecal Microbiota, and Telomere Length in Pre-Aging Phase. Frontiers in nutrition, 8, 756243.
[16] Yi, L., Maier, A. B., Tao, R., Lin, Z., Vaidya, A., Pendse, S., Thasma, S., Andhalkar, N., Avhad, G., & Kumbhar, V. (2023). The efficacy and safety of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation in healthy middle-aged adults: a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-dependent clinical trial. GeroScience, 45(1), 29–43.
[17] Yoshino, J., Mills, K. F., Yoon, M. J., & Imai, S. (2011). Nicotinamide mononucleotide, a key NAD(+) intermediate, treats the pathophysiology of diet- and age-induced diabetes in mice. Cell metabolism, 14(4), 528–536.
[18] Yoshino, M., Yoshino, J., Kayser, B. D., Patti, G. J., Franczyk, M. P., Mills, K. F., Sindelar, M., Pietka, T., Patterson, B. W., Imai, S. I., & Klein, S. (2021). Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women. Science (New York, N.Y.), 372(6547), 1224–1229.
[19] Chen, A. C., Martin, A. J., Choy, B., Fernández-Peñas, P., Dalziell, R. A., McKenzie, C. A., Scolyer, R. A., Dhillon, H. M., Vardy, J. L., Kricker, A., St George, G., Chinniah, N., Halliday, G. M., & Damian, D. L. (2015). A Phase 3 Randomized Trial of Nicotinamide for Skin-Cancer Chemoprevention. The New England journal of medicine, 373(17), 1618–1626.
[20] Bertoldo, M. J., Listijono, D. R., Ho, W. J., Riepsamen, A. H., Goss, D. M., Richani, D., Jin, X. L., Mahbub, S., Campbell, J. M., Habibalahi, A., Loh, W. N., Youngson, N. A., Maniam, J., Wong, A. S. A., Selesniemi, K., Bustamante, S., Li, C., Zhao, Y., Marinova, M. B., Kim, L. J., … Wu, L. E. (2020). NAD+ Repletion Rescues Female Fertility during Reproductive Aging. Cell reports, 30(6), 1670–1681.e7.
[21] Yoshino, J., Mills, K. F., Yoon, M. J., & Imai, S. (2011). Nicotinamide mononucleotide, a key NAD(+) intermediate, treats the pathophysiology of diet- and age-induced diabetes in mice. Cell metabolism, 14(4), 528–536.
[22] Hosseini, L., Farokhi-Sisakht, F., Badalzadeh, R., Khabbaz, A., Mahmoudi, J., & Sadigh-Eteghad, S. (2019). Nicotinamide Mononucleotide and Melatonin Alleviate Aging-induced Cognitive Impairment via Modulation of Mitochondrial Function and Apoptosis in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus. Neuroscience, 423, 29–37.
[23] Yao, Z., Yang, W., Gao, Z., & Jia, P. (2017). Nicotinamide mononucleotide inhibits JNK activation to reverse Alzheimer disease. Neuroscience letters, 647, 133–140.
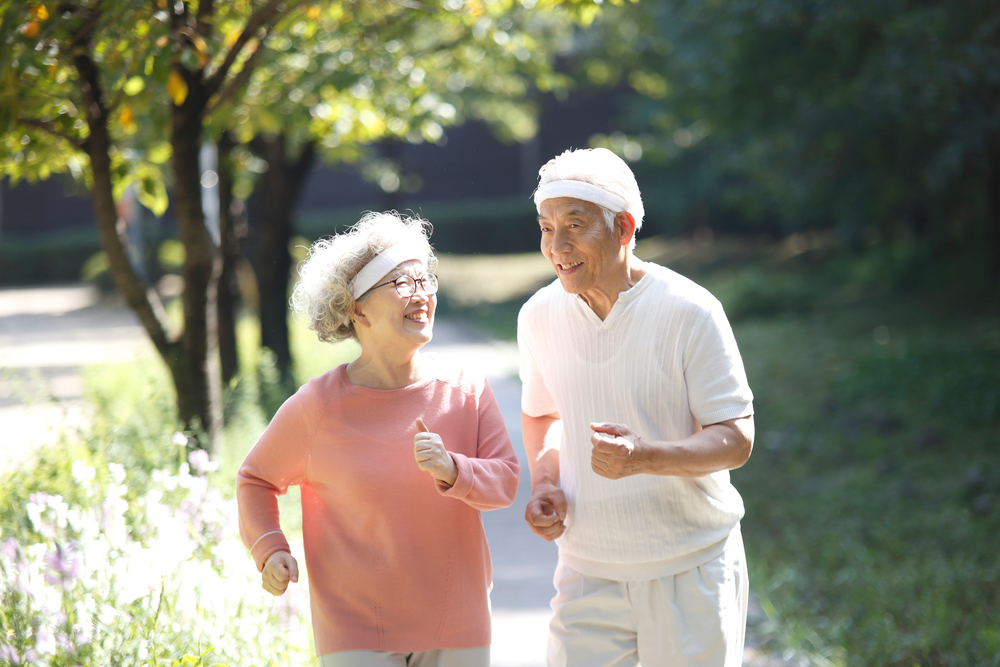
[24] Mills, K. F., Yoshida, S., Stein, L. R., Grozio, A., Kubota, S., Sasaki, Y., Redpath, P., Migaud, M. E., Apte, R. S., Uchida, K., Yoshino, J., & Imai, S. I. (2016). Long-Term Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Mitigates Age-Associated Physiological Decline in Mice. Cell metabolism, 24(6), 795–806. |






















![[국민영양] 여에스더 실크 알부민 골드 [국민영양] 여에스더 실크 알부민 골드](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002607/image/main/1000002607_main_047.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 초임계 알티지 오메가3 (흡수에 용이한 rTG 오메가3) [국민영양] 여에스더 초임계 알티지 오메가3 (흡수에 용이한 rTG 오메가3)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002021/image/main/1000002021_main_020.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 리포좀 비타민C 플러스(체내 흡수율 UP 비타민C 500%) [국민영양] 여에스더 리포좀 비타민C 플러스(체내 흡수율 UP 비타민C 500%)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002288/image/main/1000002288_main_026.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 마그네슘 (신경·근육 마그네슘 & 에너지·활력 비타민B군) [국민영양] 여에스더 마그네슘 (신경·근육 마그네슘 & 에너지·활력 비타민B군)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002122/image/main/1000002122_main_023.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 루테인&지아잔틴 (눈의 노화 케어 기능성 원료) [국민영양] 여에스더 루테인&지아잔틴 (눈의 노화 케어 기능성 원료)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/3536/image/main/3536_main_055.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 어린콜라겐 레티놀A (국내최다 인체적용시험 보유 콜라겐 원료) [국민영양] 여에스더 어린콜라겐 레티놀A (국내최다 인체적용시험 보유 콜라겐 원료)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002139/image/main/1000002139_main_05.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 멀티비타민 미네랄 (비타민&미네랄 21종) [국민영양] 여에스더 멀티비타민 미네랄 (비타민&미네랄 21종)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002032/image/main/1000002032_main_08.jpg)
![[국민영양] 식물성 멜라토닌 함유 여에스더 멜라나인 플러스 (1정당 식물성 멜라토닌 2mg) [국민영양] 식물성 멜라토닌 함유 여에스더 멜라나인 플러스 (1정당 식물성 멜라토닌 2mg)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002156/image/main/1000002156_main_013.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 칼슘 마그네슘 D (뼈 건강 필수영양소) [국민영양] 여에스더 칼슘 마그네슘 D (뼈 건강 필수영양소)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002121/image/main/1000002121_main_060.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 대마종자유 (100% 캐나다산 프리미엄 냉압착 대마종자유) [국민영양] 여에스더 대마종자유 (100% 캐나다산 프리미엄 냉압착 대마종자유)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/8894/image/main/8894_main_049.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 맥주효모 비오틴 울트라 케어 5200 맥스 (국내 최대 함량 맥주효모·비오틴 3,000%) [국민영양] 여에스더 맥주효모 비오틴 울트라 케어 5200 맥스 (국내 최대 함량 맥주효모·비오틴 3,000%)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/15763/image/main/15763_main_021.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 유기농 엑스트라버진 올리브오일 100% [국민영양] 여에스더 유기농 엑스트라버진 올리브오일 100%](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002472/image/main/1000002472_main_05.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 발아 카무트® 브랜드 밀 함유 발효 효소 (100% 캐나다산 정품 카무트 효소) [국민영양] 여에스더 발아 카무트® 브랜드 밀 함유 발효 효소 (100% 캐나다산 정품 카무트 효소)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000001109/image/main/1000001109_main_014.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 유기농 그린 컬리 케일 100% (1포당 컬리케일 4장 1,000% 농축) [국민영양] 여에스더 유기농 그린 컬리 케일 100% (1포당 컬리케일 4장 1,000% 농축)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002297/image/main/1000002297_main_095.jpg)
![[국민영양] 여에스더 NFC 유기농 레몬즙 100% (유기가공식품 인증) [국민영양] 여에스더 NFC 유기농 레몬즙 100% (유기가공식품 인증)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000000933/image/main/1000000933_main_049.jpg)
![[초특가] 여에스더 SAC 발효흑마늘 다이렉트 (소비기한 2026-04-18) [초특가] 여에스더 SAC 발효흑마늘 다이렉트 (소비기한 2026-04-18)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000001528/image/main/1000001528_main_077.jpg)
![[초특가] 여에스더 이노시톨 (소비기한 2026-02-25) [초특가] 여에스더 이노시톨 (소비기한 2026-02-25)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1025/image/main/1025_main_049.jpg)
![[초특가] 위건강 프로젝트 (위 건강 신소재 꾸지뽕추출물) [초특가] 위건강 프로젝트 (위 건강 신소재 꾸지뽕추출물)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000001709/image/main/1000001709_main_062.jpg)
![[초특가] 여에스더 아몬드 스프레드 100% (설탕·버터 무첨가 100% 아몬드) (소비기한 2026-03-31) [초특가] 여에스더 아몬드 스프레드 100% (설탕·버터 무첨가 100% 아몬드) (소비기한 2026-03-31)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000001666/image/main/1000001666_main_028.jpg)
![[초특가] 여에스더 엘라스틴 오리지널 7X [초특가] 여에스더 엘라스틴 오리지널 7X](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002765/image/main/1000002765_main_05.jpg)
![[초특가] 여에스더 가바&타트체리 젤리 [초특가] 여에스더 가바&타트체리 젤리](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1118/image/main/1118_main_012.jpg)
![[초특가] 여에스더 락토페린 맥스 (소비기한 2026-03-21) [초특가] 여에스더 락토페린 맥스 (소비기한 2026-03-21)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/10791/image/main/10791_main_011.jpg)
![[초특가] 벤포탄 액티브 정 (벤포티아민 활성형 비타민B1 함유 의약외품 피로회복제) [초특가] 벤포탄 액티브 정 (벤포티아민 활성형 비타민B1 함유 의약외품 피로회복제)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000001798/image/main/1000001798_main_030.jpg)
![[초특가] 홈모드 주름 개선&리프팅 스킨부스터 쥬베샷 [초특가] 홈모드 주름 개선&리프팅 스킨부스터 쥬베샷](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002786/image/main/1000002786_main_079.jpg)
![[초특가] 홈모드 피부 진정&흔적 관리 리페어 마스크팩 10매 [초특가] 홈모드 피부 진정&흔적 관리 리페어 마스크팩 10매](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002796/image/main/1000002796_main_067.jpg)
![[초특가] 홈모드 물광&미백 스킨부스터 리쥬샷 [초특가] 홈모드 물광&미백 스킨부스터 리쥬샷](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002789/image/main/1000002789_main_019.jpg)
![[초특가] 홈모드 피부 진정&흔적 관리 리페어 크림 [초특가] 홈모드 피부 진정&흔적 관리 리페어 크림](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002794/image/main/1000002794_main_027.jpg)
![[초특가] 홈모드 모공 타이트닝 스킨부스터 엑소샷 [초특가] 홈모드 모공 타이트닝 스킨부스터 엑소샷](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002790/image/main/1000002790_main_088.jpg)
![[초특가] 글루타치온 백옥물광 선크림 (기미·주근깨·잡티·미백·주름 개선 확인) [초특가] 글루타치온 백옥물광 선크림 (기미·주근깨·잡티·미백·주름 개선 확인)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000000905/image/main/1000000905_main_053.jpg)
![[초특가] 자외선차단 글루타치온 멀티 기미 패치 2세트 (총 8회분) [초특가] 자외선차단 글루타치온 멀티 기미 패치 2세트 (총 8회분)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/15901/image/main/15901_main_049.jpg)
![[초특가] 자외선차단 글루타치온 누드 선 패치 2세트 (총 12회분) [초특가] 자외선차단 글루타치온 누드 선 패치 2세트 (총 12회분)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/15902/image/main/15902_main_013.jpg)
![[초특가] 글루타치온 자외선 차단 톤업 에센스 본품 [초특가] 글루타치온 자외선 차단 톤업 에센스 본품](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000001989/image/main/1000001989_main_094.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 고메효소 탄수화물 단백질 분해효소 (인절미맛) (소비기한 2026-02-22) [초특가] 셀티바 고메효소 탄수화물 단백질 분해효소 (인절미맛) (소비기한 2026-02-22)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002784/image/main/1000002784_main_048.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 발포 다이어트 모로오렌지맛 3박스 [초특가] 셀티바 발포 다이어트 모로오렌지맛 3박스](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002798/image/main/1000002798_main_093.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 고메효소 탄수화물 단백질 분해효소 (샤인머스캣맛) (소비기한 2026-02-20) [초특가] 셀티바 고메효소 탄수화물 단백질 분해효소 (샤인머스캣맛) (소비기한 2026-02-20)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002763/image/main/1000002763_main_052.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 마시는 다이어트 블랙 (아메리카노맛) (소비기한 2026-04-15) [초특가] 셀티바 마시는 다이어트 블랙 (아메리카노맛) (소비기한 2026-04-15)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002795/image/main/1000002795_main_01.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 고메효소 탄수화물 단백질 분해효소 (커피과자맛) (소비기한 2026-02-21) [초특가] 셀티바 고메효소 탄수화물 단백질 분해효소 (커피과자맛) (소비기한 2026-02-21)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002782/image/main/1000002782_main_08.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 글루트랙 액티브 PK 혈당&체지방 감소 멀티팩 (소비기한 2026-04-21) [초특가] 셀티바 글루트랙 액티브 PK 혈당&체지방 감소 멀티팩 (소비기한 2026-04-21)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002799/image/main/1000002799_main_019.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 밀닷 동식물성 단백질 쉐이크 (몽블랑케이크맛) (소비기한 2026-05-20) [초특가] 셀티바 밀닷 동식물성 단백질 쉐이크 (몽블랑케이크맛) (소비기한 2026-05-20)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002792/image/main/1000002792_main_09.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 마시는 다이어트 딜라이트 (믹스커피맛) (소비기한 2026-04-15) [초특가] 셀티바 마시는 다이어트 딜라이트 (믹스커피맛) (소비기한 2026-04-15)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002793/image/main/1000002793_main_029.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 글루트랙 블랙키 AM 마시는 커피맛 혈당&쾌변습관 (소비기한 2026-05-22) [초특가] 셀티바 글루트랙 블랙키 AM 마시는 커피맛 혈당&쾌변습관 (소비기한 2026-05-22)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002802/image/main/1000002802_main_050.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 밀닷 동식물성 단백질 쉐이크 (얼그레이라떼맛) (소비기한 2026-05-17) [초특가] 셀티바 밀닷 동식물성 단백질 쉐이크 (얼그레이라떼맛) (소비기한 2026-05-17)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002788/image/main/1000002788_main_070.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 마시는 다이어트 마일드 (보리차맛) (소비기한 2026-04-16) [초특가] 셀티바 마시는 다이어트 마일드 (보리차맛) (소비기한 2026-04-16)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002797/image/main/1000002797_main_02.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 글루트랙 컨트롤밀 PRO 흑임자맛 단백질 쉐이크 (소비기한 2026-06-12) [초특가] 셀티바 글루트랙 컨트롤밀 PRO 흑임자맛 단백질 쉐이크 (소비기한 2026-06-12)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002801/image/main/1000002801_main_079.jpg)
![[초특가] 셀티바 마시는 다이어트 블랙 스위트 (스위트 아메리카노맛) (소비기한 2026-04-23) [초특가] 셀티바 마시는 다이어트 블랙 스위트 (스위트 아메리카노맛) (소비기한 2026-04-23)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002803/image/main/1000002803_main_022.jpg)
![[기획세트] 리포좀 글루타치온 9X 필름 최저가 (+ 구매자 전원 사은품 증정) [기획세트] 리포좀 글루타치온 9X 필름 최저가 (+ 구매자 전원 사은품 증정)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002464/image/main/1000002464_main_069.jpg)
![[공식몰특가] 여에스더 유산균 클래식 4병 (총 8개월분) [공식몰특가] 여에스더 유산균 클래식 4병 (총 8개월분)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002465/image/main/1000002465_main_031.jpg)
![[공식몰특가] 리포좀 NMN(엔엠엔) 필름 3박스 (총 90매) [공식몰특가] 리포좀 NMN(엔엠엔) 필름 3박스 (총 90매)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000001802/image/main/1000001802_main_097.jpg)
![[설특가][2+2] 질 유래 유산균 화이트 4박스 (총 4개월분) [설특가][2+2] 질 유래 유산균 화이트 4박스 (총 4개월분)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002246/image/main/1000002246_main_040.jpg)
![[설특가][2+2] 관절&연골건강 엠에스엠 MSM 4박스 (총 4개월분) [설특가][2+2] 관절&연골건강 엠에스엠 MSM 4박스 (총 4개월분)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002248/image/main/1000002248_main_087.jpg)
![[설특가][2+2] 눈건강 루테인&아스타잔틴 4박스 (총 4개월분) [설특가][2+2] 눈건강 루테인&아스타잔틴 4박스 (총 4개월분)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002482/image/main/1000002482_main_043.jpg)
![[설특가][2+2] 면역기능 증진 기능성 베타글루칸 4박스 (총 4개월분) [설특가][2+2] 면역기능 증진 기능성 베타글루칸 4박스 (총 4개월분)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002344/image/main/1000002344_main_052.jpg)
![[설특가][2+2] 리포좀 멀티비타민&미네랄 4박스 (총 4개월분) [설특가][2+2] 리포좀 멀티비타민&미네랄 4박스 (총 4개월분)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002481/image/main/1000002481_main_083.jpg)
![[설특가][2+2] 비타민C 3000 프리미엄 4박스 (총 120포) [설특가][2+2] 비타민C 3000 프리미엄 4박스 (총 120포)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002345/image/main/1000002345_main_058.jpg)
![[설특가][2+2] 유산균 & 당케어 플러스 4박스 (총 4개월분) [설특가][2+2] 유산균 & 당케어 플러스 4박스 (총 4개월분)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002348/image/main/1000002348_main_027.jpg)
![[설특가][2+2] 뼈건강 비타민K2 플러스 D3 4박스 (총 4개월분) [설특가][2+2] 뼈건강 비타민K2 플러스 D3 4박스 (총 4개월분)](https://godomall.speedycdn.net/d38889e2d902ed3dcc124f1c31cbbf35/goods/1000002353/image/main/1000002353_main_064.jpg)






58년생인데요
지금까지 선생님한테 유산균을 동생김동숙이 구매해줘서 계속 먹고 잇는데요
NMM도 먹어야 되는지요
58년생인데요
지금까지 선생님한테 유산균을 동생김동숙이 구매해줘서 계속 먹고 잇는데요
NMM도 먹어야 되는지요
지금 58년생인데요
지금 NMM먹으면 좋은지요 ?